A new report was recently published by Accenture1 that roughly 40% of employee tasks in the healthcare sector can be augmented by Artificial Intelligence.
At the end of April, we hosted the 25th Annual Ziegler LeadingAge National CFO Workshop in Nashville, Tennessee. The conference agenda covered a variety of topics. One of the most popular sessions of the conference was “Technology – Understanding the Role of Machine Learning & Automation in Finance and Operations.” In this month’s newsletter, we’ll dive into some of the content shared in that session with hopes to paint a picture of the abundant opportunities in this space for senior living & care provider organizations.
A new report was recently published by Accenture1 that roughly 40% of employee tasks in the healthcare sector can be augmented by Artificial Intelligence. These employee tasks were the focus of much of the discussion during our CFO Workshop session. Before delving into examples of these technological advancements, it is important to define terms commonly used. Some of these terms are often used interchangeably and they represent different levels of technological intervention in workflow. The graphic below defines the three common terms in this space: Robotic Process Automation, Machine Learning, and Artificial Intelligence.
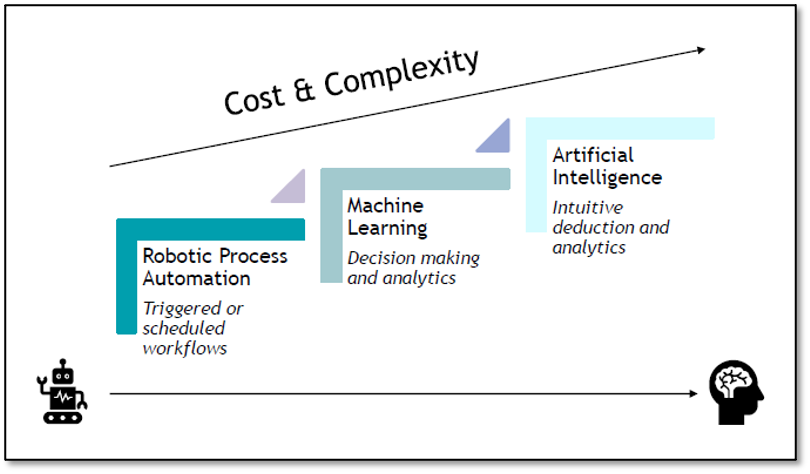
The reality is that Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is where the majority of real opportunities are in today’s senior living & care environment. As discussed by the panelists from Healthonomy and NuAig during the session, we are still very much in the first inning of these advancements in our sector. RPA is the basic opportunity to replace routine tasks that are currently manually handled by staff on a regular basis with programming that, in many cases, is instant or at a significantly reduced time commitment. RPA is best-suited for highly repetitive, rules-based tasks. If organizations were to audit what repetitive tasks and data entry they have staff doing on a regular basis, they could likely identify hundreds of opportunities for RPA enhancements.
Examples
- Healthonomy, one of the speakers in the session, shared how they have automated the intake process for new residents in the healthcare setting. Staff generally have to input data from a discharge report, determine if certain pre-approvals are met, manage approvals and determine coverage parameters. What has been done effectively is programming that automates this process, delivers reports and approvals within minutes, and all with processes that eliminate human error that often happens with manual entry.
- NuAig, the other company represented in this CFO Workshop session, shared how they recently assisted a senior living & care organization with their electronic medical record migration. This organization switched to a new platform and determined that the transfer of files would likely take more than six months. NuAig was able to create code to assist with this process and all documentation migration was completed in a little over two weeks.
These are just two real-life examples that are being utilized today in our sector. There are dozens of more examples and RPA is among the most common discussion topics among technology experts in our sector today. It is no longer just theoretical. It is happening. We encourage providers to talk with their IT experts and partners on how to best utilize the advancements of RPA to improve staff efficiencies, help mitigate the challenges of being short-staffed and in some cases, to eliminate FTEs if needed.
